 共享内存
共享内存
# 共享内存
共享内存是一种计算机进程间通信的方式,它允许多个进程可以访问同一块内存区域。相比于其他进程间通信方式,如管道、消息队列和信号量等,共享内存的速度更快,因为它避免了数据在不同进程之间的复制。
# 共享内存简介
- 共享内存是IPC通信的另一种方法,它允许两个不相关的进程访问同一个逻辑内存。
- 共享内存是在两个正在运行的进程间传递数据的一种非常有效的方式。
- 共享内存并未提供同步机制,所以需要用其他机制来同步对共享内存的访问 ,这将由程序员来负责。
# 共享工作原理
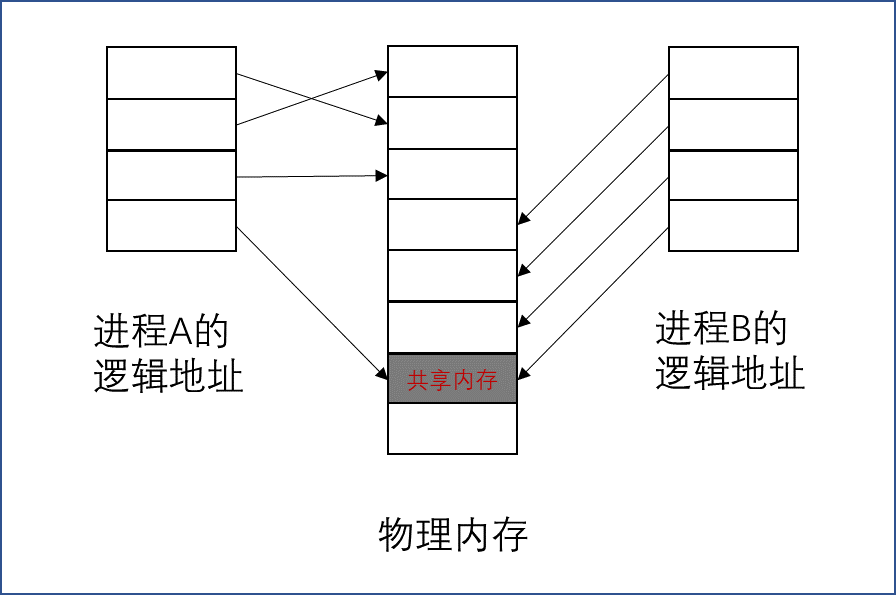
共享内存是由IPC为进程创建的一个特殊的地址范围,出现在该进程的地址空间中,其他进程可以将同一段共享内存连接到他们自己的地址空间中。
所有进程都可以访问共享内存中的地址,就好像他们是由malloc分配的一样。如果一个进程向共享内存中写了数据,那么其他进程将立刻能够看到。
# 共享内存示意图
# 创建共享内存
# shmget函数
#include <sys/tpyes.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
key:与信号量一样,程序需要提供一个key,以此键值来获取一个有效的共享内存标识符。size:要申请的共享内存大小,以字节为单位。shmflg:权限位,与创建文件的mode标志一样,并可与IPC_CREAT相或- 返回值:创建成功则返回共享内存标识符,失败返回-1.
# shmat函数
第一次创建共享内存时,它还不能被任何程序使用,必须使用shmat函数将其连接到一个进程的地址空间中。
#include <sys/tpyes.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void* shmat(int shm_id, const void* shm_addr, int shmflg);
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
shm_id:shmget返回的共享内存标识符。shm_addr:指定共享内存连接到当前进程中的地址位置,此参数值通常是个空指针,表示让系统来选择共享内存的地址。shmflg:一组标志位,包含例如读写权限等。- 返回值:如果调用成功,返回指向共享内存第一个字节的指针,如果失败,返回-1.
# shmdt函数
该函数用来将共享内存从当前进程中分离。将共享内存从进程中分离并未删除它,仅使得当前进程不再能使用该共享内存。
#include <sys/tpyes.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void* shmdt(const void* shm_addr);
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
shm_addr:shmat函数返回的地址指针。- 返回值:成功时返回0,失败时返回-1.
# shmctl函数
共享内存控制函数。
#include <sys/tpyes.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shm_id, int command, struct shmid_ds* buf);
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
shm_id:shmget返回的共享内存标识符。command:要采取的动作,例如删除共享内存。buf:指向包含共享内存模式和访问权限的结构。- 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1。
# 共享内存举例
编写生产者、消费者程序。
- 第一个程序(消费者)创建一个共享内存段,并将其中的内容显示出来。
- 第二个程序(生产者)连接到一个已有的共享内存段,并允许我们向其中写入数据。
# 定义数据结构(share.h)
// share.h
#define TEXT_SZ 2048 //申请共享内存大小
struct shared_use_st
{
int written_by_you;
char some_text[TEXT_SZ];
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 消费者程序
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include "share.h"
int main()
{
int running = 1;
void *shared_memory = (void *)0;
struct shared_use_st *shared_stuff;
int shmid;
srand((unsigned int)getpid());
shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, sizeof(struct shared_use_st), 0666 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
shared_memory = shmat(shmid, (void *)0, 0);
if (shared_memory == (void *)-1) {
fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Memory attached at %X\n", (int)shared_memory);
shared_stuff = (struct shared_use_st *)shared_memory;
shared_stuff->written_by_you = 0;
while(running)
{
if (shared_stuff->written_by_you)
{
printf("You wrote: %s", shared_stuff->some_text);
sleep( rand() % 4 );
shared_stuff->written_by_you = 0;
if (strncmp(shared_stuff->some_text, "end", 3) == 0)
{
running = 0;
}
}
}
if (shmdt(shared_memory) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmdt failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmctl(IPC_RMID) failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("customer exit.\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# 生产者程序
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include "share.h"
int main()
{
int running = 1;
void *shared_memory = (void *)0;
struct shared_use_st *shared_stuff;
char buffer[BUFSIZ];
int shmid;
shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, sizeof(struct shared_use_st), 0666 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
shared_memory = shmat(shmid, (void *)0, 0);
if (shared_memory == (void *)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Memory attached at %X\n", (int)shared_memory);
shared_stuff = (struct shared_use_st *)shared_memory;
while(running)
{
while(shared_stuff->written_by_you == 1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("waiting for client...\n");
}
printf("Enter some text: ");
fgets(buffer, BUFSIZ, stdin);
strncpy(shared_stuff->some_text, buffer, TEXT_SZ);
shared_stuff->written_by_you = 1;
if (strncmp(buffer, "end", 3) == 0)
{
running = 0;
}
}
if (shmdt(shared_memory) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmdt failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("producer exit.\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# 输出
# 终端1
$ ./customer
Memory attached at 141E2000
You wrote: 123
You wrote: 456
You wrote: end
customer exit.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 终端2
$ ./producer
Memory attached at C3B0F000
Enter some text: 123
waiting for client...
Enter some text: 456
waiting for client...
Enter some text: end
producer exit.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 分析
两个程序的共享内存输出的地址是各自进程空间中的逻辑地址。
shared_stuff->written_by_you == 1说明生产者写入了信息,并且消费者还没有读走。使用共享内存需要对进程间的同步和互斥进行管理,避免数据冲突和竞争条件的发生。
共享内存由消费者创建,最后由消费者通过shmctl()删除。
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2023/03/31, 22:34:04
